Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Grafana¶
This chapter gives instruction for getting a basic configuration of Logstash working in a SIMP environment.
If these instructions don’t work for you, please take a look at the README in
the SIMP Logstash module, particularly the acceptance tests in the
spec/acceptance directory.
Obtaining the Required Packages¶
As an optional component in the SIMP infrastructure, the ELG packages are not included in the SIMP distribution.
You will need to proceed to the vendor sites to obtain the require RPMs and put them in an accessible YUM repository. The SIMP modules were designed with the assumption that you would be using a repository for all of your installations.
The following versions have been tested against the SIMP ELG Stack:
- Elasticsearch : 2.3
- Logstash : 2.3
- Grafana : 3.1
Logstash¶
Logstash is an Open Source tool that provides a means for SIMP implementations to have logs and events collected, searched, and forwarded (filtered or unfiltered) to another host. SIMP comes with three separate but related modules. The modules are:
- Logstash: Installs the RPMs and configuration needed for log inputs, filters, and outputs.
- Grafana: Installs the RPMs and configuration needed for the Grafana web interface.
- Elasticsearch: Installs the RPMs and configuration needed for Elasticsearch.
Warning
The Logstash class is incompatible with the SIMP rsyslog::stock::server
class!
You cannot enable both of them on the same sever.
Logstash Architecture¶
The Logstash architecture is quite straightforward. It takes inputs from various sources, optionally applies filters, and outputs the results to a specified target. It’s likely that you can already forward logs to Logstash and output them in a useful format as part of your existing architecture.
Logstash filters can manipulate logs after ingest and before output. Examples of existing filters include fixing logs to split/combine lines, adding fields, normalizing time stamps, and adding GeoIP fields. Depending on the type of log manipulation that is desired, there is likely a filter and Logstash documentation that already exists.
SIMP Logstash Architecture¶
Combining the SIMP Logstash, Elasticsearch, and Grafana modules provides an functioning log collection, reduction, and search capability. Unless scale dictates otherwise, these three modules can easily be applied to a single host.
The intent of providing Logstash in SIMP is to replace the default
Centralized Rsyslog server with a capability that is easier to search and analyze
over time. Once your Logstash server is set up, you simply need to direct your
hosts to forward logs to your Logstash server. In a default SIMP configuration,
this can be done by setting the $log_server variable in Hiera.
It is up to each implementation to define and apply filters that meet their local requirements. While multiple output targets may be defined, SIMP only defines the Elasticsearch output by default. Please see the Elasticsearch Puppet module for details on how to define additional output targets.
The following diagram depicts the standard SIMP data flow through the Logstash system.
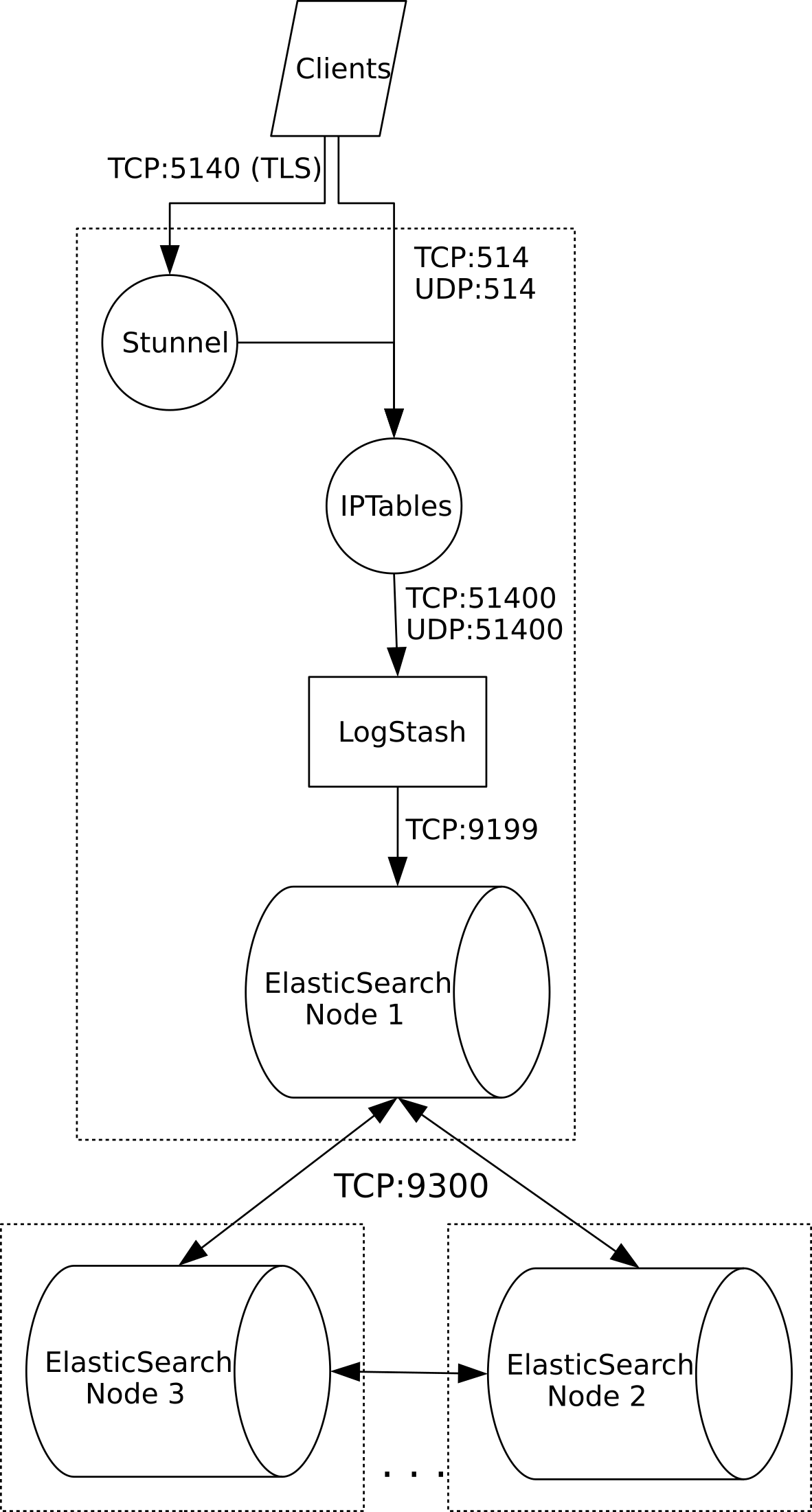
SIMP Logstash Deployment¶
Logstash, SIMP, and Security¶
The provided SIMP modules for Logstash, Elasticsearch, and Grafana have been built with connection security in mind. Overriding these settings could adversely affect the security of the logging infrastructure. The following list describes the security features in place with the default SIMP module settings:
Warning
The native (Java) Elasticsearch connections are not encrypted!
This will be remedied in the future as sufficient methods are found. Presently, you can look at the SIMP IPSec implementation to encrypt communication between your Elasticsearch nodes.
- User Name and Password Protection for Grafana: The Grafana web can
be exposed to a defined list of hosts. If you are connecting to Grafana from anything other than the localhost, a user name and password is required for authentication. Both LDAP and local database users are supported.
- Syslog over Stunnel: The default behavior in SIMP is to encrypt syslog traffic over Stunnel. This remains the case with Logstash. Unencrypted traffic is also supported for network devices.
- Limiting Web Actions: The Grafana module restricts what HTTP commands a user can perform on the Elasticsearch data store. Full POST action must be given to the Logstash nodes and some nodes may require DELETE capabilities. Logstash hosts should be tightly controlled so that administrative users cannot modify data inside of Elasticsearch with carefully crafted commands. This is one reason that we use syslog on the local hosts.
Important
The Puppet modules for Logstash, Grafana, and Elasticsearch contain dozens of variables that may be manipulated.
You should read each product’s documentation and ensure you understand any setting that is changed from the default SIMP values. Changes can affect both security and functionality of the system.
Logstash Setup¶
Logstash System Requirements¶
The storage requirements for Logstash and Elasticsearch vary depending
on how long you plan on keeping logs. When using Elasticsearch, the logs are
formatted for Elasticsearch and stored in /var/elasticsearch. You can also
configure how many days of data you wish to keep in Elasticsearch
(keep_days => '99'). Therefore, you should ensure you have enough space on
/var to keep your defined number of days worth of logs.
As you grow your Elasticsearch cluster to handle increasing log loads,
you will want to ensure that your keep_days is set to handle your
entire cluster appropriately.
Note
You should have at least 4G of memory available on any Elasticsearch node.
Important
It is not advised to install the ELG stack on your Puppet management infrastructure as both tend to use large amounts of system resources.
Recommended SIMP Logstash Setup¶
The following example can be applied to a single host with a large
/var volume and 4GB of memory.
You can extend and replicate this setup on as many systems as necessary to provide ingest and dashboard redundancy. Alternatively, you can split Grafana and Logstash to do allow greater resource dedication.
We do recommend that you have an Elasticsearch node on the Logstash system to reduce the likelihood that Logstash will hang when trying to find a non-existent storage node.
Optimization of your Elasticsearch infrastructure depends on many factors and should be handled once you decide how far your systems is going to expand. Please be aware that scaling is highly dependent on how your actually use your cluster in production.
We would recommend a search on Elasticsearch Scaling prior to setting up your initial cluster.
---
# Add these settings to your Logstash node
## Set up Logstash ##
# This is required due to a bug in the 'elastic' logstash module
logstash::logstash_user : 'logstash'
logstash::logstash_group : 'logstash'
# Listen on unencrypted UDP for legacy network devices
simp_logstash::input::syslog::listen_plain_udp
# Send all output to the local Elasticsearch instance
simp_logstash::outputs :
- 'elasticsearch'
# Keep 30 days of logs
simp_logstash::clean::keep_days: '30'
## Set up Elasticsearch ##
# Make this unique per cluster!
simp_elasticsearch::cluster_name : 'some_unique_cluster_name'
# We're assuming that you only have one interface here. If you don't, set
# this to the appropriate value for your system
simp_elasticsearch::bind_host : "%{::ipaddress}"
# This needs to be a list of *all* of the Elasticsearch nodes in the cluster.
# This is done to restrict communications to only trusted nodes
#
# Any node not entered here will not be connected to and will not be allowed
# to communicate with this host.
#
# SIMP does not support multicast connectivity for security reasons.
simp_elasticsearch::unicast_hosts :
- "%{::fqdn}:9300"
- "es1.%{::domain}:9300"
- "es2.%{::domain}:9300"
## Classes that you need to include for this setup
classes:
- 'simp_elasticsearch'
- 'simp_logstash'
# Include this if you wish to auto-purge your Elasticsearch records
- 'simp_logstash::clean'
Deploying Additional Elasticsearch Nodes¶
In the case of the Elasticsearch node setup below, it may be better to
use a group match to pull your Hiera settings. To do this, you should
add the following to your site.pp file for your environment.
if $trusted['certname'] =~ /es\d+\.your\.domain/ {
$hostgroup = 'elasticsearch'
}
Then, ensure that a file called ‘elasticsearch.yaml’ is present in the
/etc/puppet/environments/simp/hieradata/hostgroups/ directory and
contains the following content.
---
# All nodes running elasticsearch in your cluster should use
# these settings.
simp_elasticsearch::cluster_name: 'some_unique_cluster_name'
# The replicas can be no more than the total number of Elasticsearch nodes
# that you have in your cluster.
simp_elasticsearch::replicas: '2'
simp_elasticsearch::unicast_hosts :
- "%{::fqdn}:9300"
- "es1.%{::domain}:9300"
- "es2.%{::domain}:9300"
classes:
- 'simp_elasticsearch'
Make sure you point your clients to the Logstash server by setting the
log_server variable to the fqdn of the Logstash server in
Hiera.
Deploying Grafana¶
Now that you have a functional logging setup, you’ll probably want to deploy a GUI to provide the ability to generate user dashboards as well as dynamic log analysis.
The SIMP team chose to support the Open Source Grafana project due to its inbuilt authentication support but you could easily point Kibana or another interface of your choosing at your Elasticsearch cluster.
Note
It is suggested that you install Grafana on a host that is not an Elasticsearch node unless using a single-node deployment.
This is to prevent any vulnerabilities in Grafana from providing direct access to your Elasticsearch infrastructure
Note
By default, the Grafana administrative password is randomly set using simplib passgen(). You can use the simp passgen command to obtain the password for your environment.
Note
The rubygem-toml package must be present on your puppet compile servers
for the Grafana puppet module to function properly.
If you do not install this via Kickstart, you will need two runs of Puppet to complete the Grafana installation since the TOML Ruby Gem will not be able to be installed prior to Puppet loading.
Warning
Do not point Grafana directly at your Logstash node unless you have a single-node deployment.
Grafana has the ability to put extreme loads on your Elasticsearch infrastructure with poorly formed queries and should be connected to a node that is not used for ingest.
Targeting your Grafana host or hostgroup, apply the following Hiera settings.
---
# Array of networks that are allowed to access your Grafana dashboard. Uses
# the standard SIMP 'client_nets' semantics.
#
# In this case, we're allowing everyone in and trusting that Grafana will do
# its job properly.
simp_grafana::client_nets:
- 'ALL'
classes:
- 'simp_grafana'
After your Puppet run, you should be able to connect to port 443 on your Grafana host and authenticate with the administrative user.
Documentation on LDAP integration is forthcoming...